富有機(jī)質(zhì)細(xì)粒沉積巖往往為深水沉積,可以較為完整的保存沉積時(shí)期的古氣候、水體性質(zhì)和古生態(tài)等信息。尤其在早侏羅世、早白堊世、晚白堊世和古新世-漸新世,全球發(fā)生了一系列的缺氧、溫室-熱室、古火災(zāi)、水陸生態(tài)系統(tǒng)快速演替、碳釋放和碳富集等熱點(diǎn)事件,而這些全球性及區(qū)域事件在富有機(jī)質(zhì)細(xì)粒沉積巖中可以得到有效的保存。
針對(duì)上述科學(xué)問(wèn)題,吉林大學(xué)地球科學(xué)學(xué)院劉招君教授團(tuán)隊(duì)的孫平昌副教授及研究生王君賢、李元吉、陶連馨和王灼等人,對(duì)東北地區(qū)撫順盆地始新統(tǒng)巨厚含煤-含油頁(yè)巖層系、新疆準(zhǔn)噶爾盆地二疊紀(jì)蘆草溝組巨厚油頁(yè)巖層序和新疆大長(zhǎng)溝盆地早侏羅世八道灣組含油頁(yè)巖-燭煤層系開(kāi)展了古環(huán)境恢復(fù),取得以下階段性進(jìn)展:
進(jìn)展1—定量恢復(fù)了東北地區(qū)始新世和新疆地區(qū)早侏羅世古大氣CO2濃度
基于有機(jī)碳同位素及飽和烴單體碳同位素,確定陸源有機(jī)質(zhì)碳同位素值,利用古大氣二氧化碳估算公式,計(jì)算出撫順盆地極熱時(shí)期pCO2在2500-1000ppm左右,其中以ETM2時(shí)期二氧化碳濃度最高(圖1);估算出早侏羅世Sinemurian的pCO2介于1815-625ppm。并初步揭示早侏羅世和始新世二氧化碳濃度升高與地表有機(jī)質(zhì)氧化和火山事件有關(guān)。
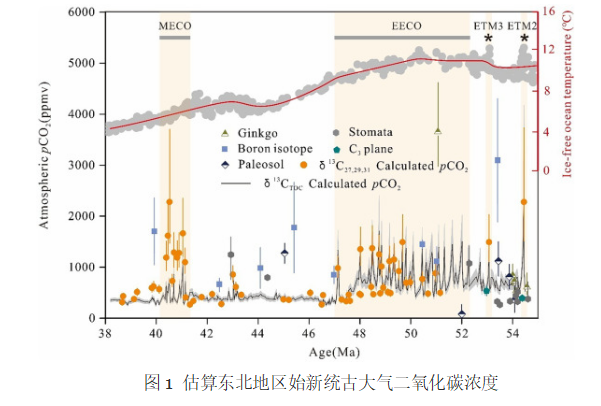
B同位素(Pearson et al.,2009;Pearson and Palmer,2000),銀杏(Retallack,2001;Retallack,2009;Beerling et al.,2009;Beerling and Royer,2002;Royer,2003;Smith et al.,2010),古土壤(Koch et al.,1992;Cerling,1992;Sinha and Stott,1994;Ekart et al.,1999;Royer et al.,2001a;Nordt et al.,2002),氣孔(Royer et al.,2001b;Royer,2003;Doria et al.,2011;Maxbauer et al.,2014;Barclay and Wing,2016),C3植物(Cui and Schubert,2016)
進(jìn)展2-建立撫順盆地始新統(tǒng)天文年代標(biāo)尺,識(shí)別出多期極熱事件,刻畫(huà)了極熱事件對(duì)陸地生態(tài)的影響
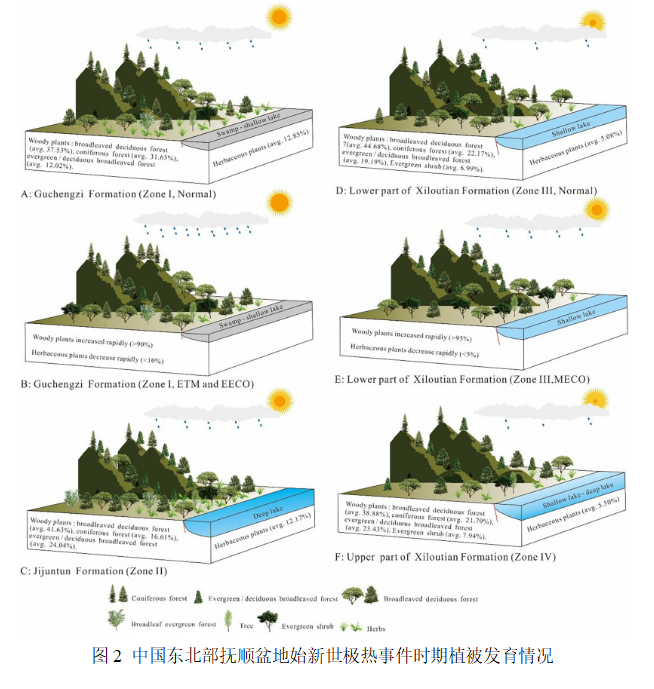
在古城子火山灰絕對(duì)年齡、生物和古地磁年齡基礎(chǔ)上,開(kāi)展了米氏旋回分析,建立了天文年代標(biāo)尺,并結(jié)合CIE,在撫順盆地始新統(tǒng)識(shí)別出ETM2、ETM3、EECO等極熱事件,同時(shí)結(jié)合磁化率和色度與同位素的變化趨勢(shì)、聚類(lèi)分析,確定磁化率是進(jìn)行古氣候分析的有效指標(biāo)。根據(jù)孢粉組合特征,確定東北地區(qū)始新統(tǒng)極熱時(shí)期古氣溫上升2-5℃,降雨量增加了200-600mm,同時(shí)高溫事件促使針葉樹(shù)等木本植物的生長(zhǎng),促進(jìn)了碳封存,揭示出始新世氣候變暖的短期爆發(fā)導(dǎo)致亞洲中緯度地區(qū)植被發(fā)生重大變化,改變了景觀,并改變了區(qū)域水文狀況(圖2)。
進(jìn)展3-揭示了相對(duì)淺水環(huán)境中有機(jī)質(zhì)富集控制因素
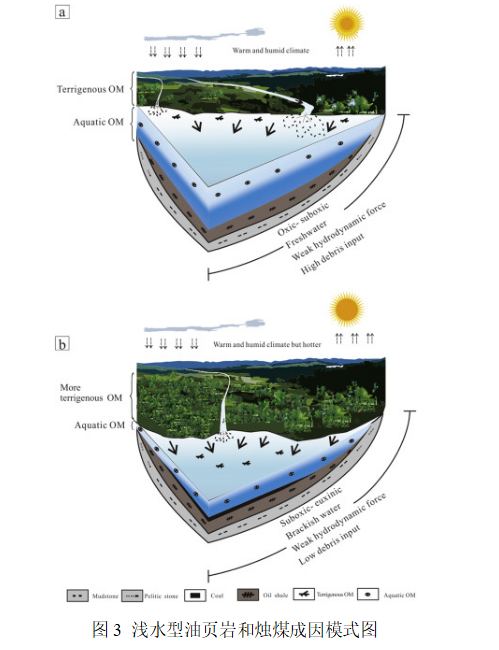
根據(jù)我國(guó)陸相盆地油頁(yè)巖賦存特征,識(shí)別出深水和淺水兩種類(lèi)型的油頁(yè)巖礦床,并以撫順盆地西露天組和大長(zhǎng)溝盆地八道灣組淺水油頁(yè)巖為實(shí)例開(kāi)展有機(jī)質(zhì)富集機(jī)制研究,總體表明水陸生態(tài)變化及有機(jī)質(zhì)來(lái)源的更替(圖3)、淺水蒸發(fā)咸化是控制淺水型油頁(yè)巖發(fā)育厚度、品質(zhì)和展布特征的關(guān)鍵因素。
進(jìn)展4-揭示了富有機(jī)質(zhì)細(xì)粒沉積巖形成的水動(dòng)力條件
油頁(yè)巖層系中往往發(fā)育碎屑顆粒紋層(碎屑顆粒含量A(體積百分含量)≥75vol.%)、富碎屑顆粒紋層(75>A≥50 vol.%)、富黏土質(zhì)紋層(50>A≥25 vol.%)和黏土質(zhì)紋層(A<25 vol.%)。通過(guò)開(kāi)展單紋層粒度分析,發(fā)現(xiàn)紋層中碎屑顆粒多以遞變懸浮和均勻懸浮搬運(yùn)為主,多受季節(jié)性洪水、地表徑流注入和遠(yuǎn)端濁積巖末端效應(yīng)的影響,此外風(fēng)攜沉積也是部分細(xì)粒沉積物的主要來(lái)源(圖4)。

上述系列研究成果發(fā)表在國(guó)際地學(xué)知名期刊《Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology》、《Marine and Petroleum Geology》及《Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources》、《ACS Omega》、《古地理學(xué)報(bào)》等期刊上。該系列研究受?chē)?guó)家自然基金(41772092)資助。
論文:
1) Yuanji Li(李元吉)*,Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Howard J.Falcon-Lang,Zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Baoyong Zhang(張保勇),Qiang Zhang(張強(qiáng)),Junxian Wang(王君賢),Yinbo Xu(徐銀波). Eocene hyperthermal events drove episodes of vegetation turnover in the Fushun Basin, northeast China: Evidence from a palaeoclimate analysis of palynological assemblages. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2022, 111317.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111317
2) Junxian Wang(王君賢),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Yueyue Bai(白悅悅),zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Rihui Cheng(程日輝),Yuanji Li(李元吉). Carbon isotopes of n-alkanes allow for estimation of the pCO2 pressure in the Early Jurassic - A case study from lacustrine shale and cannel boghead in the Dachanggou Basin, Xinjiang, North west China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,607,111252.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111252
3) Lianxin Tao(陶連馨),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Yinbo Xu(徐銀波). Sedimentary origin of fine-grained rocks in the Permian Lucaogou Formation in the southern Junggar Basin: implications from grain size analysis. Geomechanics and Geophysics for Geo-Energy and Geo-Resources,2022,192.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1007/s40948-022-00475-2
4) Yuanji Li(李元吉),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Yueyue Bai(白悅悅),Lin Ma(馬琳),Junxian Wang(王君賢),Yinbo Xu(徐銀波),Rong Liu(柳蓉). Quantitative reconstruction of atmospheric pCO2 sources during Eocene hyperthermal events based on data from the Fushun Basin, Northeast China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology,2022,601,111099.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2022.111099
5) Zhuo Wang(王灼),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Jiangfeng Du(杜江峰),Yuanji Li(李元吉),Junxian Wang(王君賢),Liyun Hou(侯麗云),Yinbo Xu(徐銀波),Yueyue Bai(白悅悅). Eocene Paleoclimate Evolution under the Background of Warmhouse–Hothouse Conditions in the Continental Fushun Basin: Implications from Magnetic Susceptibility and Color Reflectance. ACS Omega,2022, 28(7):24614–24625.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.2c02445
6) Yuanji Li(李元吉),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Yueyue Bai(白悅悅),Yinbo Xu(徐銀波),Lin Ma(馬琳),Rong Liu(柳蓉). Eocene hyperthermal events in the terrestrial system: Geochronological and astrochronological constraints in the Fushun Basin, NE China. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2022, 139, 105604.
論文鏈接: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo. 2022.105604
7) Junxian Wang(王君賢),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Yuanji Li(李元吉). Characteristics and genesis of lacustrine laminar coal and oil shale: A case study in the Dachanggou Basin, Xinjiang, Northwest China. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2021,126,104924.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j. marpetgeo.2021.104924
8) Yuanji Li(李元吉),Pingchang Sun(孫平昌)*,Zhaojun Liu(劉招君),Yinbo Xu(徐銀波),Rong Liu(柳蓉),Lin Ma(馬琳). Factors controlling the distribution of oil shale layers in the Eocene Fushun Basin, NE China. Marine and Petroleum Geology,2021,134,105350.
論文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo. 2021.105350
9) 劉招君,孫平昌*. 中國(guó)陸相盆地油頁(yè)巖形成環(huán)境與成礦機(jī)制. 古地理學(xué)報(bào),2021,23(1):1-17.
論文鏈接:https:// doi: 10.7605 /gdlxb.2021.01.001